Analysis of the canid Y-chromosome phylogeny using short-read sequencing data reveals the presence of distinct haplogroups among Neolithic European dogs
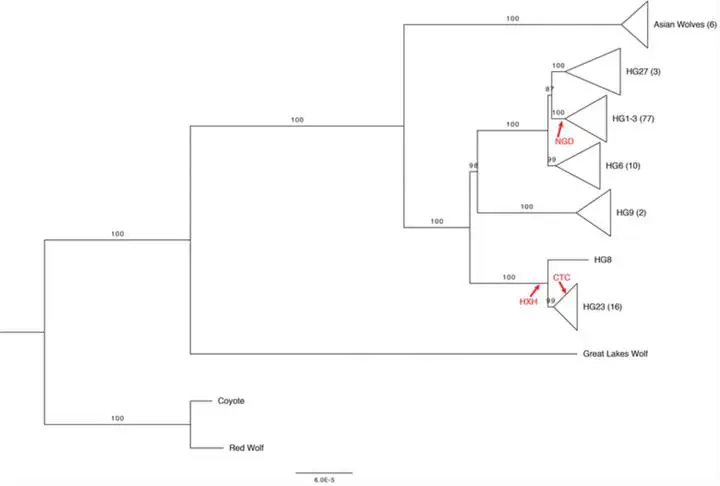 Image credit: Springer
Image credit: Springer
Abstract
Most genetic analyses of ancient and modern dogs have focused on variation in the autosomes or on the mitochondria. Mitochondrial DNA is more easily obtained from ancient samples than nuclear DNA and mitochondrial analyses have revealed important insights into the evolutionary history of canids. Utilizing a recently published dog Y-chromosome reference, we analyzed Y-chromosome sequence across a diverse collection of canids and determined the Y haplogroup of three ancient European dogs. We identified 1121 biallelic Y-chromosome SNVs using whole-genome sequences from 118 canids and defined variants diagnostic to distinct dog Y haplogroups. Similar to that of the mitochondria and previous more limited studies of Y diversity, we observe several deep splits in the Y-chromosome tree which may be the result of retained Y-chromosome diversity which predates dog domestication or post-domestication admixture with wolves. We find that Y-chromosomes from three ancient European dogs (4700–7000 years old) belong to distinct clades. We estimate that the time to the most recent comment ancestor of dog Y haplogroups is 68–151 thousand years ago. Analysis of three Y-chromosomes from the Neolithic confirms long stranding population structure among European dogs.